Empowering Young People For
Accountablity & Climate Action
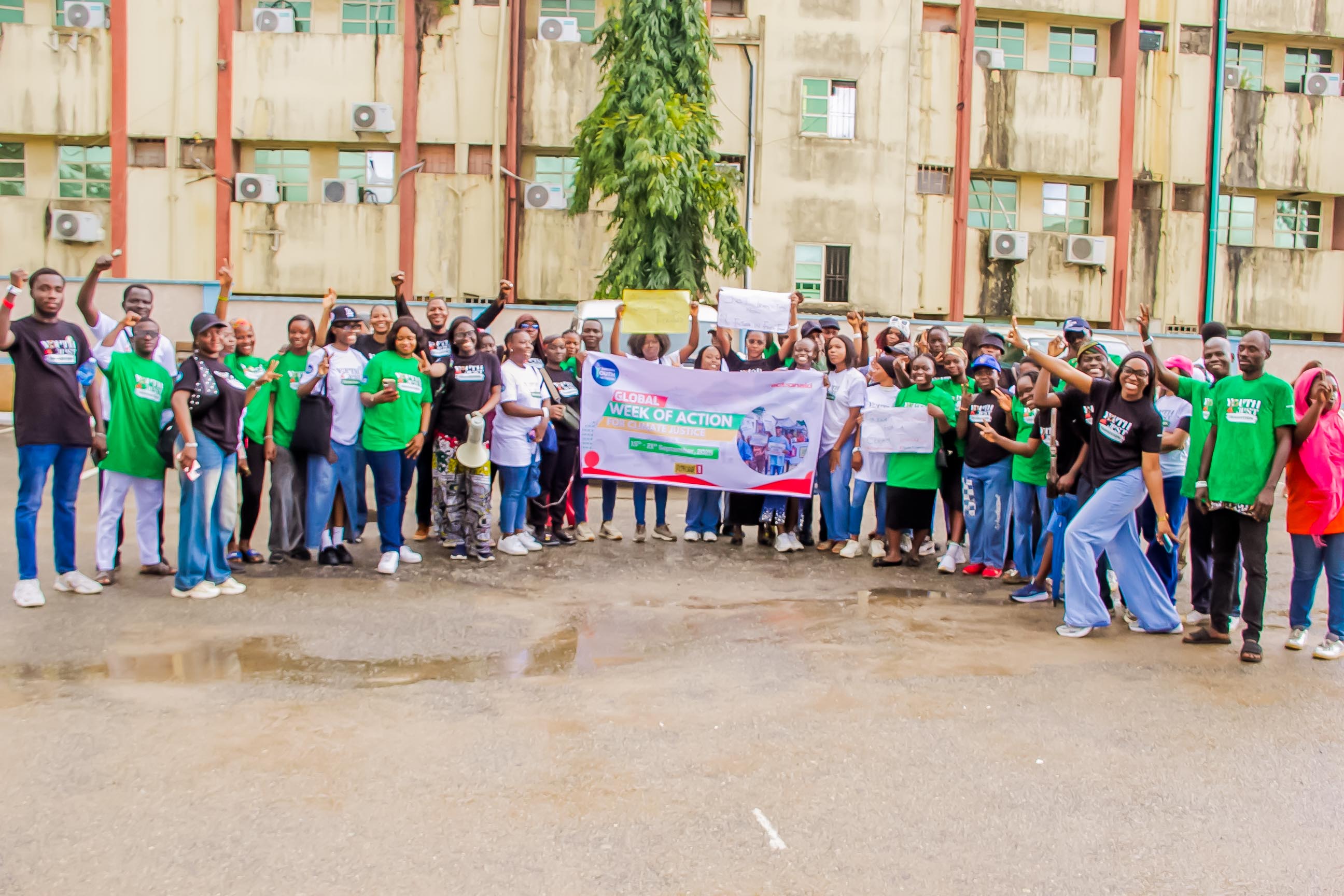
Awareness
We empower young people with vital knowledge and skills, enabling them to become strong advocates and future leaders.
Learn More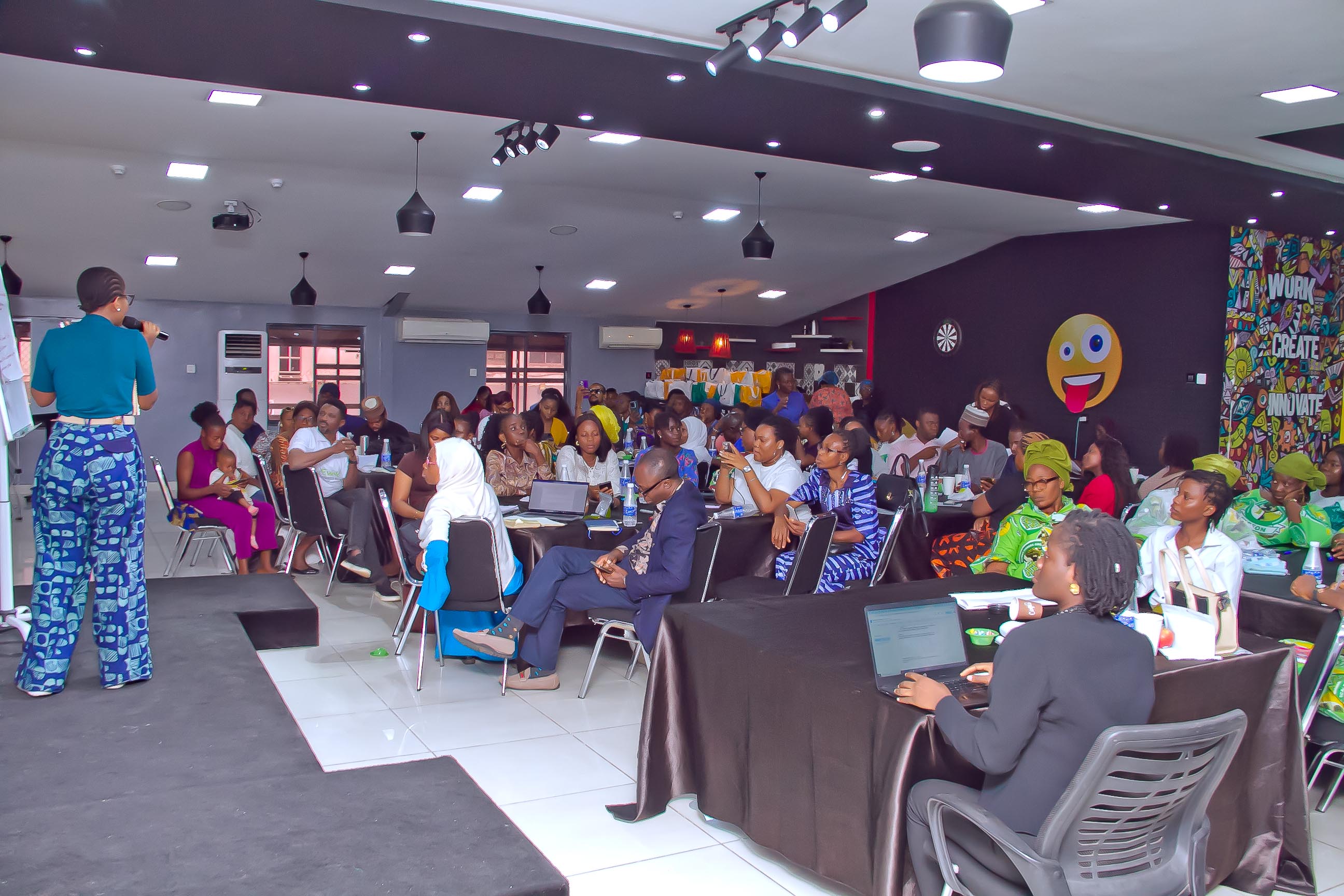
Capacity Building
We equip young people with knowledge and skills to become effective advocates and leaders through comprehensive programs.
Learn More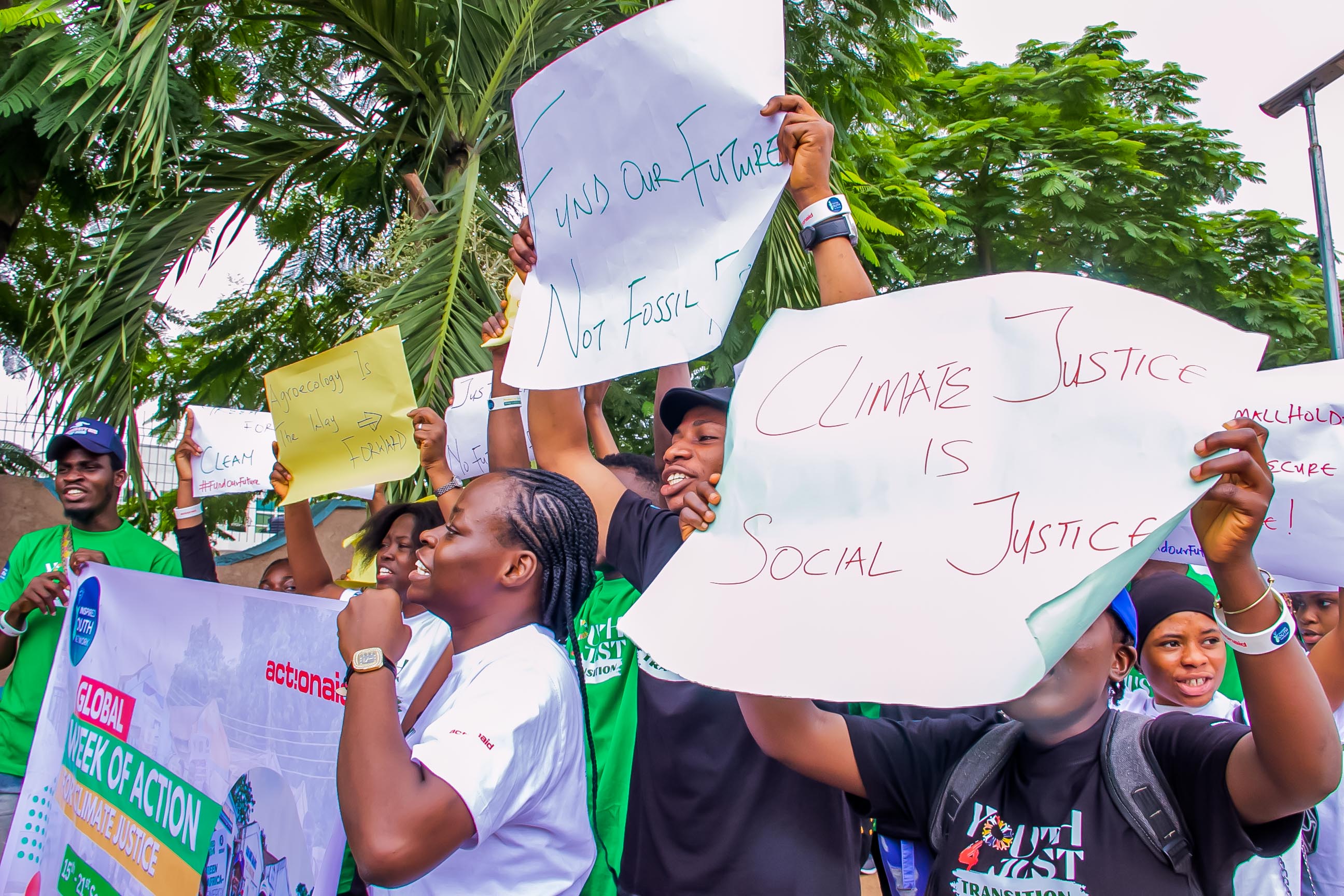
Policy Advocacy
Collaborate with us to empower youth well-being and growth. Explore volunteer opportunities to inspire meaningful change.
Learn More
Empowering Young Voices For A Better Future
IYN believes in the power of young people to drive transformative change in Nigeria. We equip them with tools for inclusion, accountability, and transparency. Through partnerships like the SPAII project with ActionAid, we strengthen youth capacity, especially for young women and marginalized groups, ensuring access to resources and participation in democratic processes.
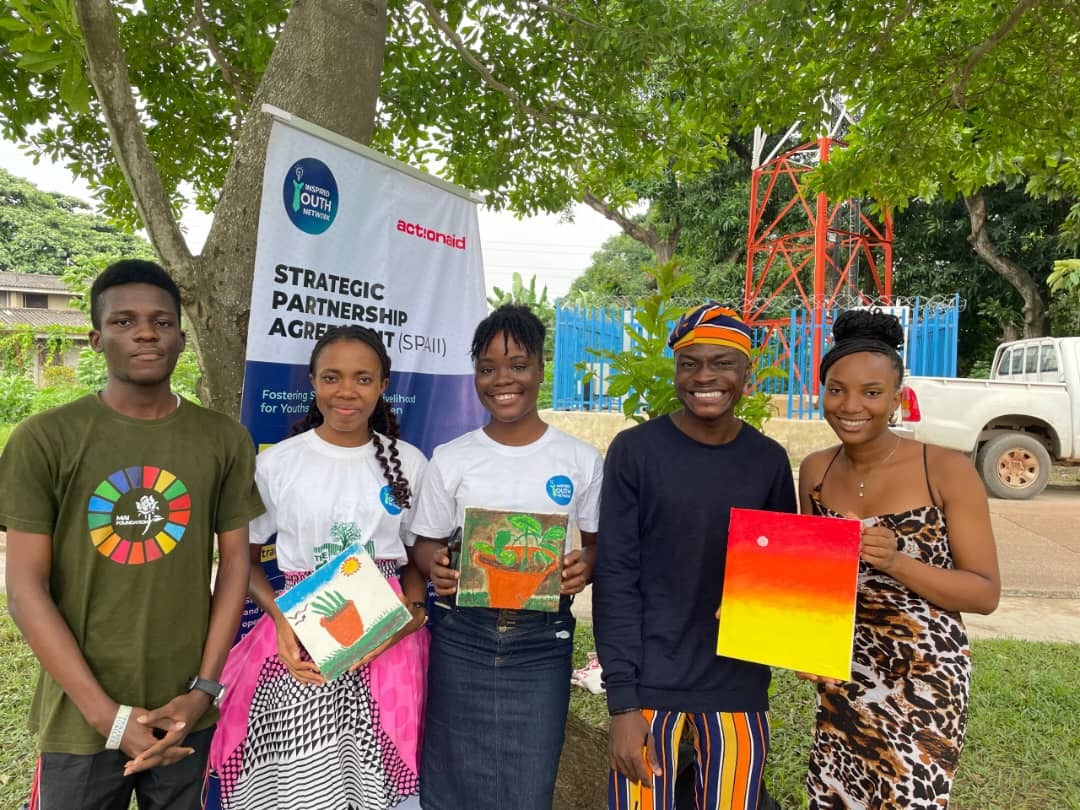

Become a volunteer
Empower youth for change. Support IYN's advocacy and capacity building work. Provide resources such as reports, infographics, and educational materials related to the charity's cause
Learn More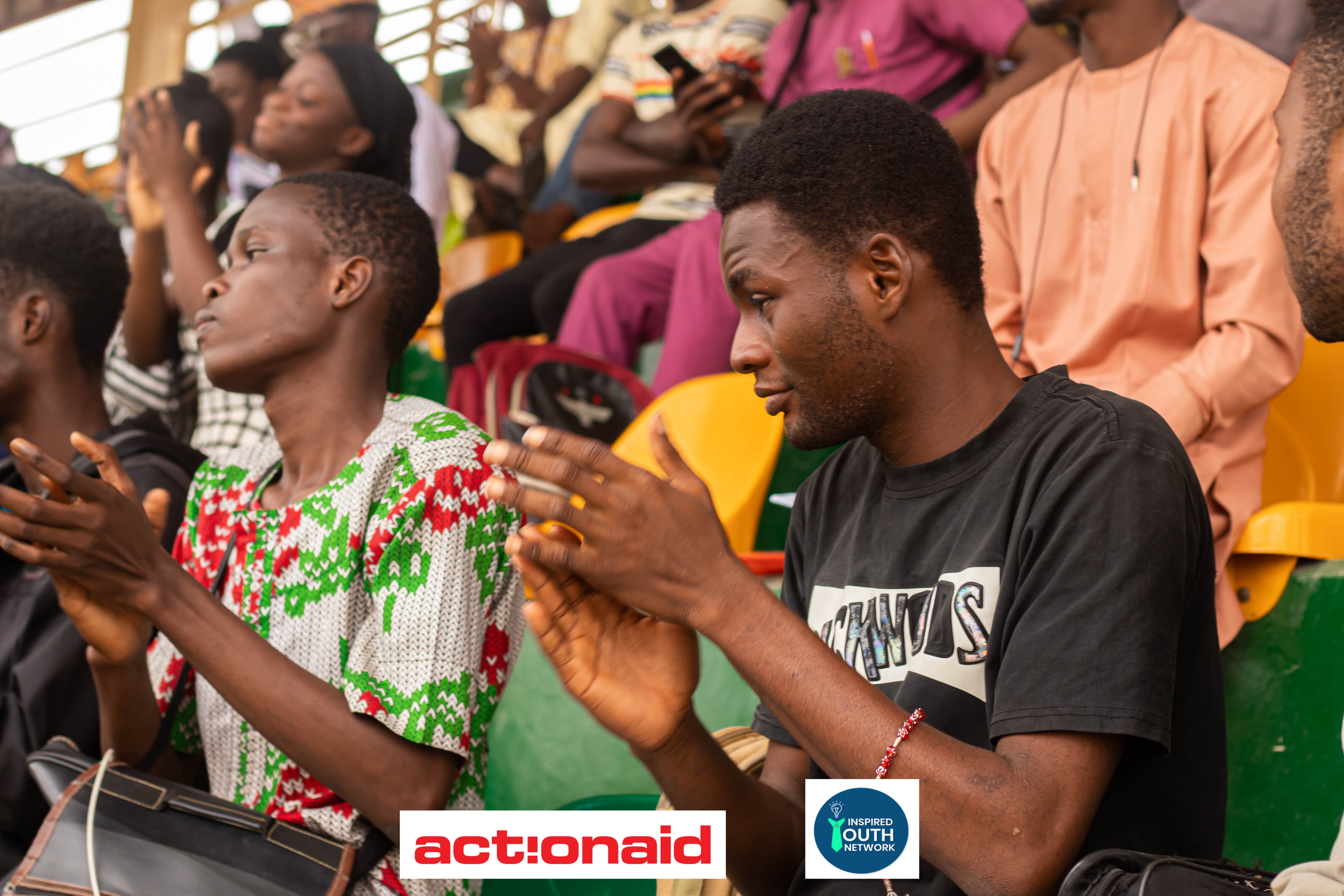
Join Us
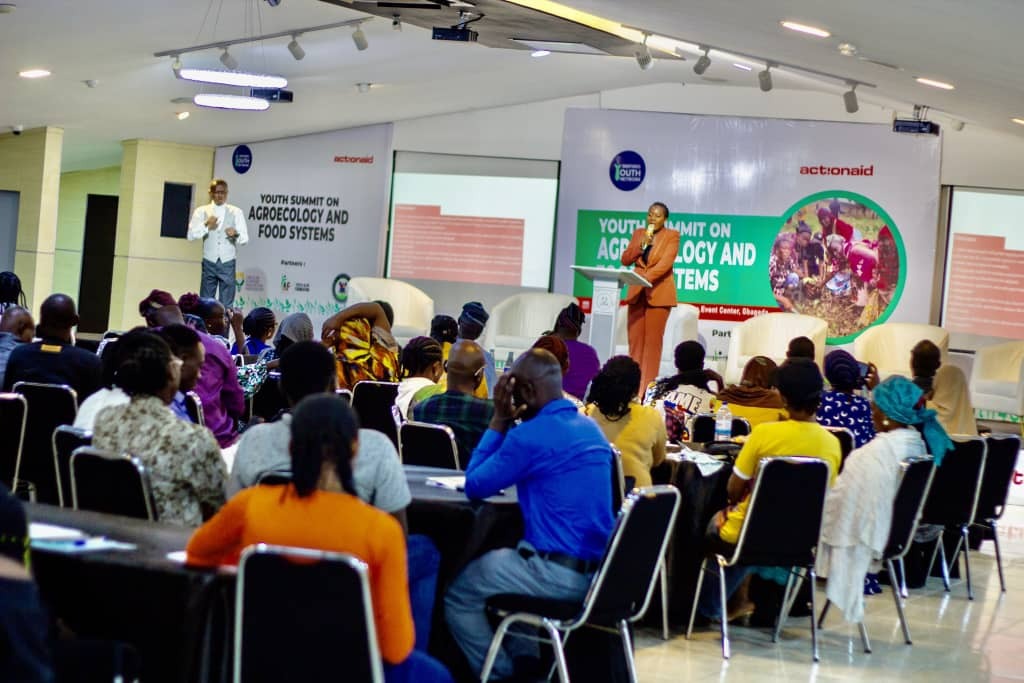
Be a voice for youth. Assist IYN's projects for inclusion and accountability. Provide resources such as reports, infographics, and educational materials related to the charity's cause
Learn MoreWe Empower Young Leaders With Skills & Advocacy
We empower young Nigerians through skill-building, advocacy training, and platforms for demanding accountability and driving impactful change now.


Ayomikun Olugbode
Our impact stories showcase the power of empowered youth & their resilience.
Meet The People Behind The Mission
Dedicated professionals working tirelessly to empower young voices across Nigeria




